Hyundai Accent: Troubleshooting
Hyundai Accent: Troubleshooting
Basic Troubleshooting
Basic Troubleshooting Guide

Customer Problem Analysis Sheet
Basic Inspection Procedure
Measuring Condition of Electronic Parts' Resistance
The measured resistance at high temperature after vehicle
running may be high or low. So all resistance must be measured at ambient temperature
(20°C, 68°F), unless stated otherwise.
|
The measured resistance in except for ambient temperature
(20°C, 68°F) is reference value.
|
Intermittent Problem Inspection Procedure
Sometimes the most difficult case in troubleshooting is when
a problem symptom occurs but does not occur again during testing. An example
would be if a problem appears only when the vehicle is cold but has not appeared
when warm. In this case, the technician should thoroughly make out a "Customer
Problem Analysis Sheet" and recreate (simulate) the environment and condition
which occurred when the vehicle was having the issue.
|
1. |
Clear Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
|
|
2. |
Inspect connector connection, and check terminal
for poor connections, loose wires, bent, broken or corroded pins, and
then verify that the connectors are always securely fastened.
|
|
3. |
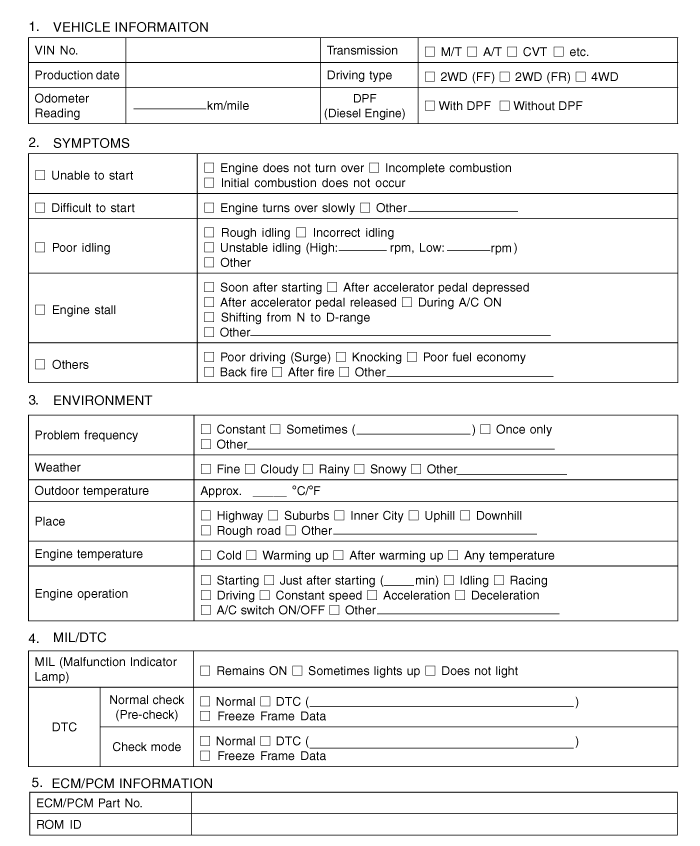
Slightly shake the connector and wiring harness vertically
and horizontally.
|
|
4. |
Repair or replace the component that has a problem.
|
|
5. |
Verify that the problem has disappeared with the
road test.
|
● Simulating Vibration
| 1) |
Sensors and Actuators
: Slightly vibrate sensors, actuators or relays with
finger.
|
Strong vibration may break sensors, actuators
or relays
|
|
| 2) |
Connectors and Harness
: Lightly shake the connector and wiring harness
vertically and then horizontally.
|
● Simulating Heat
| 1) |
Heat components suspected of causing the malfunction
with a hair dryer or other heat source.
|
• |
DO NOT heat components to the point
where they may be damaged.
|
|
• |
DO NOT heat the ECM directly.
|
|
|
● Simulating Water Sprinkling
| 1) |
Sprinkle water onto vehicle to simulate a rainy day
or a high humidity condition.
|
DO NOT sprinkle water directly into the engine
compartment or electronic components.
|
|
● Simulating Electrical Load
| 1) |
Turn on all electrical systems to simulate excessive
electrical loads (Radios, fans, lights, rear window defogger, etc.).
|
Connector Inspection Procedure
|
1. |
Handling of Connector
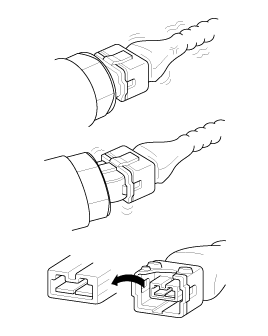
| A. |
Never pull on the wiring harness when disconnecting
connectors.
|
| B. |
When removing the connector with a lock,
press or pull locking lever.
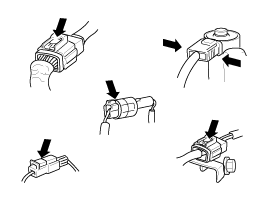
|
| C. |
Listen for a click when locking connectors.
This sound indicates that they are securely locked.
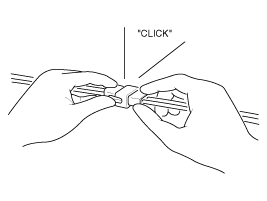
|
| D. |
When a tester is used to check for continuity,
or to measure voltage, always insert tester probe from wire
harness side.
|
| E. |
Check waterproof connector terminals from
the connector side. Waterproof connectors cannot be accessed
from harness side.
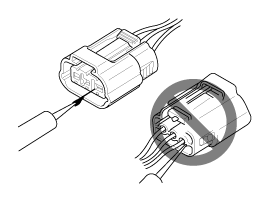
|
• |
Use a fine wire to prevent
damage to the terminal.
|
|
• |
Do not damage the terminal
when inserting the tester lead.
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Checking Point for Connector
| A. |
While the connector is connected:
Hold the connector, check connecting condition
and locking efficiency.
|
| B. |
When the connector is disconnected:
Check missed terminal, crimped terminal or
broken core wire by slightly pulling the wire harness.
Visually check for rust, contamination, deformation
and bend.
|
| C. |
Check terminal tightening condition:
Insert a spare male terminal into a female
terminal, and then check terminal tightening conditions.
|
| D. |
Pull lightly on individual wires to ensure
that each wire is secured in the terminal.
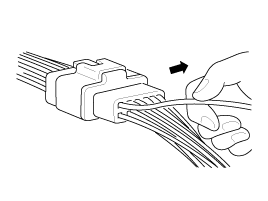
|
|
|
3. |
Repair Method of Connector Terminal
| A. |
Clean the contact points using air gun and/or
shop rag.
|
Never use sand paper when polishing
the contact points, otherwise the contact point may
be damaged.
|
|
| B. |
In case of abnormal contact pressure, replace
the female terminal.
|
|
Wire Harness Inspection Procedure
|
1. |
Before removing the wire harness, check the wire
harness position and crimping in order to restore it correctly.
|
|
2. |
Check whether the wire harness is twisted, pulled
or loosened.
|
|
3. |
Check whether the temperature of the wire harness
is abnormally high.
|
|
4. |
Check whether the wire harness is rotating, moving
or vibrating against the sharp edge of a part.
|
|
5. |
Check the connection between the wire harness and
any installed part.
|
|
6. |
If the covering of wire harness is damaged; secure,
repair or replace the harness.
|
Electrical Circuit Inspection Procedure
● Check Open Circuit
|
1. |
Procedures for Open Circuit
If an open circuit occurs (as seen in [FIG. 1]),
it can be found by performing Step 2 (Continuity Check Method) or Step
3 (Voltage Check Method) as shown below.
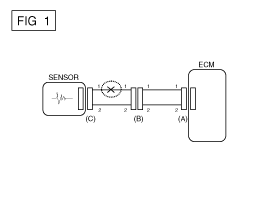
|
|
2. |
Continuity Check Method
|
When measuring for resistance, lightly shake
the wire harness above and below or from side to side.
|
Specification (Resistance)
1Ω or less → Normal Circuit
1MΩ or Higher → Open Circuit
|
| A. |
Disconnect connectors (A), (C) and measure
resistance between connector (A) and (C) as shown in [FIG. 2].
In [FIG.2.] the measured resistance of line
1 and 2 is higher than 1MΩ and below 1 Ω respectively. Specifically
the open circuit is line 1 (Line 2 is normal). To find exact
break point, check sub line of line 1 as described in next step.
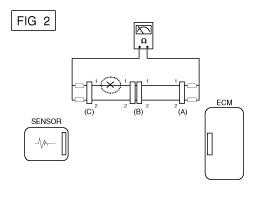
|
| B. |
Disconnect connector (B), and measure for
resistance between connector (C) and (B1) and between (B2) and
(A) as shown in [FIG. 3].
In this case the measured resistance between
connector (C) and (B1) is higher than 1MΩ and the open circuit
is between terminal 1 of connector (C) and terminal 1 of connector
(B1).
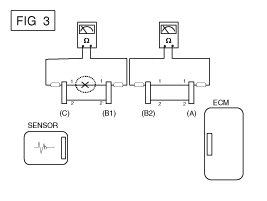
|
|
|
3. |
Voltage Check Method
| A. |
With each connector still connected, measure
the voltage between the chassis ground and terminal 1 of each
connectors (A), (B) and (C) as shown in [FIG. 4].
The measured voltage of each connector is
5V, 5V and 0V respectively. So the open circuit is between connector
(C) and (B).
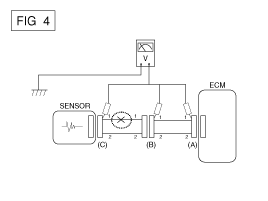
|
|
● Check Short Circuit
|
1. |
Test Method for Short to Ground Circuit
| A. |
Continuity Check with Chassis Ground
|
If short to ground circuit occurs as shown in [FIG.
5], the broken point can be found by performing Step 2 (Continuity Check
Method with Chassis Ground) as shown below.
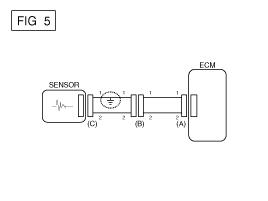
|
|
2. |
Continuity Check Method (with Chassis Ground)
|
Lightly shake the wire harness above and
below, or from side to side when measuring the resistance.
|
Specification (Resistance)
1Ω or less → Short to Ground Circuit
1MΩ or Higher → Normal Circuit
|
| A. |
Disconnect connectors (A), (C) and measure
for resistance between connector (A) and Chassis Ground as shown
in [FIG. 6].
The measured resistance of line 1 and 2 in
this example is below 1 Ω and higher than 1MΩ respectively.
Specifically the short to ground circuit is line 1 (Line 2 is
normal). To find exact broken point, check the sub line of line
1 as described in the following step.
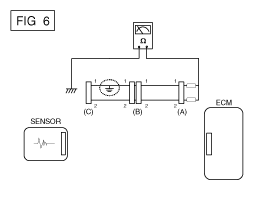
|
| B. |
Disconnect connector (B), and measure the
resistance between connector (A) and chassis ground, and between
(B1) and chassis ground as shown in [FIG. 7].
The measured resistance between connector
(B1) and chassis ground is 1Ω or less. The short to ground circuit
is between terminal 1 of connector (C) and terminal 1 of connector
(B1).
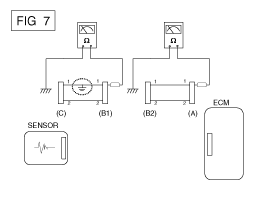
|
|
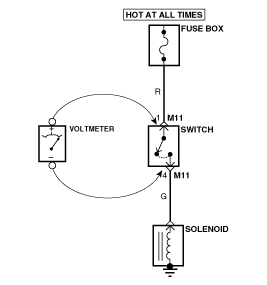
● Testing For Voltage Drop
This test checks for voltage drop along a wire, or through
a connection orswitch.
| 1) |
Connect the positive lead of a voltmeter to the end
of the wire (or to the side of the connector or switch) closest to the
battery.
|
| 2) |
Connect the negative lead to the other end of the
wire. (or the other side of the connector or switch)
|
| 4) |
The voltmeter will show the difference in voltage
between the two points. A difference, or drop of more than 0.1 volts
(50mV in 5V circuits), may indicate a problem. Check the circuit for
loose or dirty connections.
|
Symptom Troubleshooting Guide Chart
Main symptom
|
Diagnostic procedure
|
Also check for
|
Unable to start
(Engine does not turn over)
|
| 3. |
Inhibitor switch (A/T) or clutch start switch
(M/T)
|
|
|
Unable to start
(Incomplete combustion)
|
| 2. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 3. |
Check the ignition circuit
|
| 4. |
Troubleshooting the immobilizer system
(In case of immobilizer lamp flashing)
|
|
| •
|
Slipped or broken timing belt
|
|
Difficult to start
|
| 2. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 3. |
Check the ECTS and circuit (Check DTC)
|
| 4. |
Check the ignition circuit
|
|
|
Poor idling
(Rough, unstable or incorrect Idle)
|
| 1. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 3. |
Check the long term fuel trim and short term
fuel trim
(Refer to CUSTOMER DATASTREAM)
|
| 4. |
Check the idle speed control circuit (Check
DTC)
|
| 5. |
Inspect and test the Throttle Body
|
| 6. |
Check the ECTS and circuit (Check DTC)
|
|
|
Engine stall
|
| 2. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 3. |
Check the idle speed control circuit (Check
DTC)
|
| 4. |
Check the ignition circuit
|
| 5. |
Check the CKPS Circuit (Check DTC)
|
|
|
Poor driving
(Surge)
|
| 1. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 2. |
Inspect and test Throttle Body
|
| 3. |
Check the ignition circuit
|
| 4. |
Check the ECTS and Circuit (Check DTC)
|
| 5. |
Test the exhaust system for a possible restriction
|
| 6. |
Check the long term fuel trim and short term
fuel trim (Refer to CUSTOMER DATASTREAM)
|
|
|
Knocking
|
| 1. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 2. |
Inspect the engine coolant
|
| 3. |
Inspect the radiator and the electric cooling
fan
|
|
|
Poor fuel economy
|
| 1. |
Check customer's driving habitsIs
· A/C on full time or the defroster mode
on?
· Are tires at correct pressure?
· Is excessively heavy load being carried?
· Is acceleration too much, too often?
|
| 2. |
Check the fuel pressure
|
| 4. |
Test the exhaust system for a possible restriction
|
| 5. |
Check the ECTS and circuit
|
|
|
Hard to refuel
(Overflow during refueling)
|
| 1. |
Test the canister close valve
|
| 2. |
Inspect the fuel filler hose/pipe
· Pinched, kinked or blocked?
· Filler hose is torn
|
| 3. |
Inspect the fuel tank vapor vent hose between
the canister and fuel tank air filter
|
|
| •
|
Malfunctioning gas station filling nozzle
(If this problem occurs at a specific gas station during refueling)
|
|
Special Service Tools
Item
Illustration
Application
Fuel Pressure Gauge
(09353-24100)
Measuring the fuel line press ...
See also:
In case of an emergency while driving
If the engine stalls at a crossroad or crossing
If the engine stalls at a crossroad or crossing, set the shift lever in the N
(Neutral) position and then push the vehicle to a safe place.
If you h ...
Installation
1.
Remove the ignition key from the vehicle.
2.
Disconnect the battery negative cable and wait for at least three
minutes.
...
ESC OFF Switch. Description
and Operation
Description
1.
The ESC OFF switch is for the user to turn off the ESC system.
2.
The ESC OFF lamp is on when ESC OFF switch is engaged.
...
 Hyundai Accent: Troubleshooting
Hyundai Accent: Troubleshooting


 Special Service Tools
Special Service Tools